Ground Rod Resistance Requirement

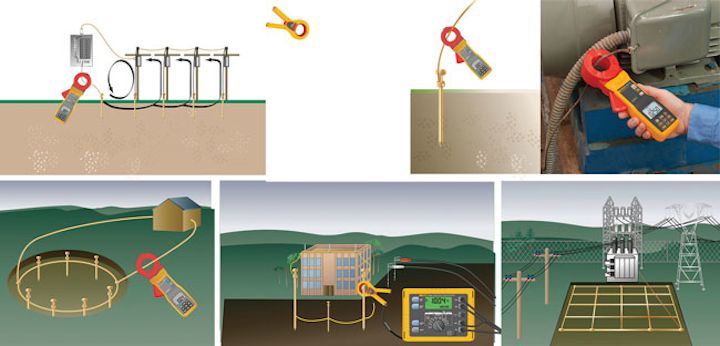
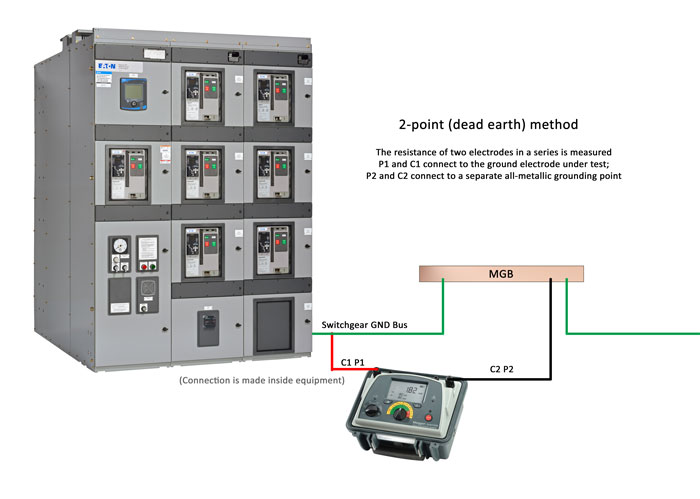
In areas where driving ground rods may be impractical the two point method can be used.
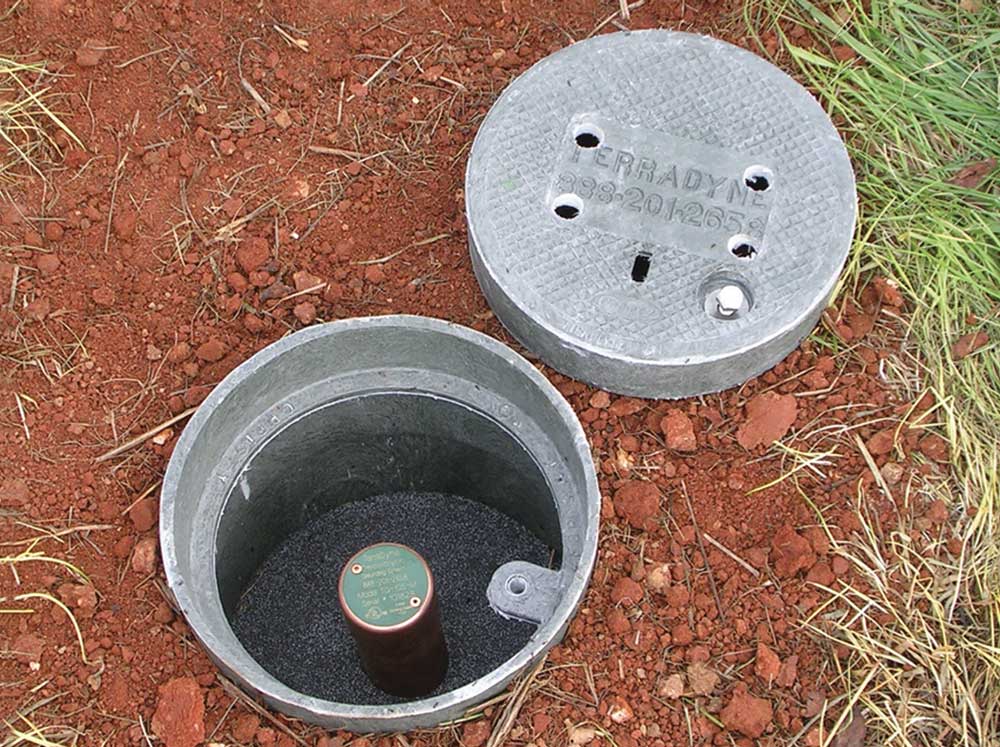
Ground rod resistance requirement. In practice for a residential structure most electricians place two ground rods and call it done. Unfortunately there is not one standard ground resistance threshold recognized by all certifying agencies. This requirement clarifies that the supplemental electrode system must be. I do not know of an equivalent requirement in the british standards.
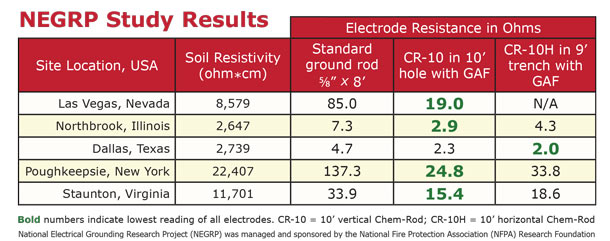
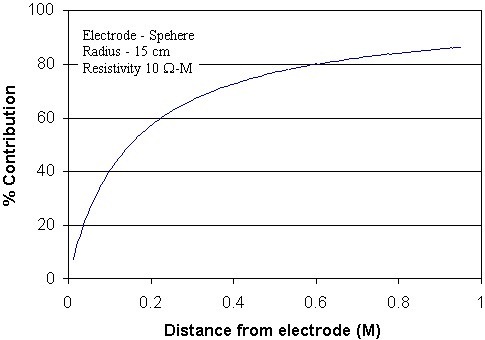
If this is the case for your ground rod the best solution is to drive a different rod into a different location. Ideally a ground should be zero ohms of resistance but. In some instances ground rods can be installed in areas where the earth has a lot of resistance. The nfpa and ieee recommend a ground resistance value of 5 ohms or less while the nec has stated to make sure that system impedance to ground is less than 5 ohms specified in nec 50 56.
For instance if a ground rod is driven into a very rocky and dry area it may not conduct electricity into the ground well. On jobs where a building or structure. There is no requirement to retest the resistance. Nearly all electricians and electrical inspectors are familiar with the national electrical code requirement in sec.
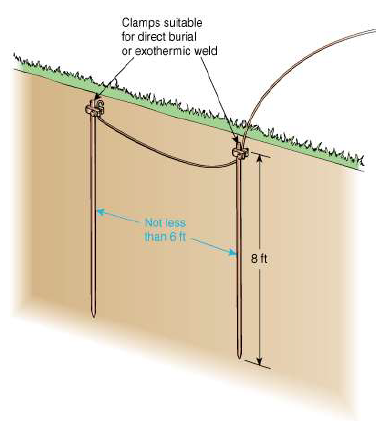
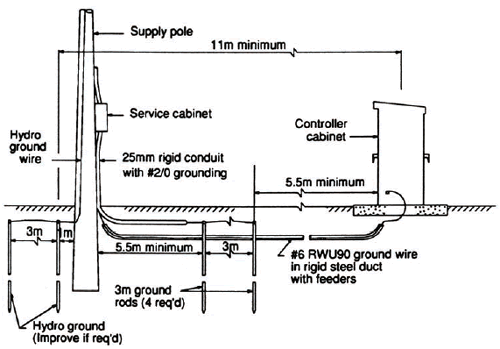
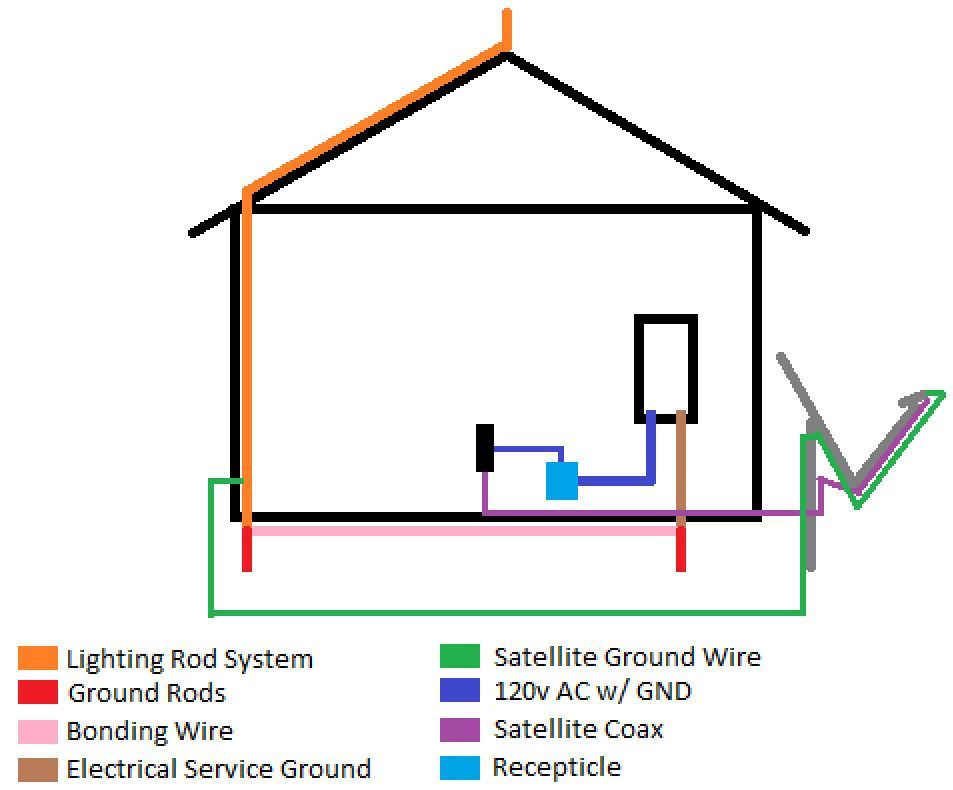
In areas where codes require two ground rods because of high electrical resistance in the soil the rods must be spaced at least 6 feet apart and interconnected by a buried jumper wire. P2 and c2 connect to a separate all metallic grounding point like a water pipe or building steel. Resistance of a single ground rod exceeds 25 ohms to ground and the metal underground water line is the only other available electrode an additional electrode must be installed. With this method the resistance of two electrodes in a series is measured by connecting the p1 and c1 terminals to the ground electrode under test.
The length of a ground rod plays a much bigger role in its final ground resistance measurement and it goes without saying that it takes longer to drive a longer ground rod. If this additional electrode is another ground rod it must be driven at least 6 away. 250 54 which requires the resistance to ground of a single made electrode e g ground rod to be 25 ohms or less. This does not create the best ground but it meets the bare minimum of the code.
Ground rod current source lightning average current 30 000 amps.